恒溫控制器系統概述
該恒溫控制器系統包含以下幾個功能:
- 可按鍵設定溫度
- 可顯示當前溫度和用戶設定溫度
- 有升溫、降溫模塊
- 可最終達到恒溫
仿真軟件
- Keil 5
- Proteus 8.6
系統設計
電路設計

恒溫控制系統一共有6個模塊,分別是主控芯片模塊、按鍵輸入模塊、設定溫度顯示模塊、當前溫度顯示模塊、溫度采集模塊和升溫、降溫模塊。
- 按鍵輸入模塊:該模塊由4*3的矩陣鍵盤和1個確認按鈕構成。系統剛開始啟動后,用戶通過矩陣鍵盤輸入想要設定的溫度(0°~99°),輸入完畢后按下確認鍵,然后將該溫度數據傳送給主控芯片AT89C51;
- 設定溫度顯示模塊:該模塊由一個2位8段LED數碼管構成,主控芯片AT89C51使用P3口控制該數碼管的段選,使用P2.4和P2.5兩個端口來控制該數碼管的位選。主控芯片AT89C51將從矩陣鍵盤得到的設定溫度信息,通過2位8段LED數碼管顯示出來;
- 溫度采集模塊;該模塊由一個DS18B20溫度傳感器構成。使用DS18B20溫度傳感器采集當前的溫度,并將該溫度信息傳送給主控芯片AT89C51;
- 當前溫度顯示模塊:該模塊由兩個74HC573鎖存器和一個4位8段LED數碼管構成,主控芯片AT89C51使用P2.6和P2.7控制兩個74HC573鎖存器的片選,兩個鎖存器的輸入口均與主控芯片的P0口相連,并使用一個100歐的排阻作為P0口的上拉電阻,兩個鎖存器的輸出口分別與4位8段LED數碼管的段選口與位選口相連;
- 升溫、降溫模塊:該模塊由一個綠色LED和一個紅色LED構成,綠色LED負責降溫,每閃爍一次溫度下降0.5°,紅色LED負責升溫,每閃爍一次溫度上升0.5°。主控芯片AT89C51根據當前溫度和用戶設定溫度之間的差值,來控制升溫還是降溫,以達到恒溫的目的。
軟件代碼編寫
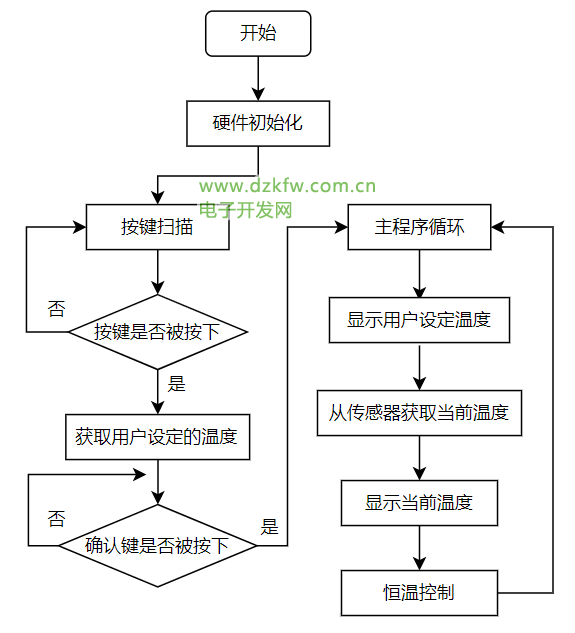
程序的具體流程如下:
- 硬件初始化,關閉所有的數碼管;
- 進行兩次按鍵掃描循環,分別獲取用戶設定溫度的十位和個位,獲取完畢后,判斷確認鍵是否被按下,如果用戶按下確認鍵則進入到主程序循環中;
while(ok) //用戶設定溫度
{
while(key1 == 15)
{
key1 = keyscan();
delay(50);
}
while(key2 == 15)
{
key2 = keyscan();
delay(50);
}
delay(100);//等待確認鍵
}
//鍵盤掃描
uchar keyscan()
{
uchar temp,key;
key = 15; // 默認值,如果沒有按鍵按下key就為該默認值
P1 = 0xfe; //掃描第一行
temp = P1;
temp = temp & 0xf0;
if(temp!=0xf0)
{
delay(10); // 延時消抖
temp = P1;
temp = temp & 0xf0;
if(temp!=0xf0)
{
temp = P1;
switch(temp) //掃描列
{
case 0xee:
key = 1;
break;
case 0xde:
key = 2;
break;
case 0xbe:
key = 3;
break;
}
while(temp!=0xf0) //等待按鍵釋放
{
temp = P1;
temp = temp & 0xf0;
}
}
}
P1 = 0xfd; //掃描第二行
temp = P1;
temp = temp & 0xf0;
if(temp!=0xf0)
{
delay(10); // 延時消抖
temp = P1;
temp = temp & 0xf0;
if(temp!=0xf0)
{
temp = P1;
switch(temp) //掃描列
{
case 0xed:
key = 4;
break;
case 0xdd:
key = 5;
break;
case 0xbd:
key = 6;
break;
}
while(temp!=0xf0) //等待按鍵釋放
{
temp = P1;
temp = temp & 0xf0;
}
}
}
P1 = 0xfb; //掃描第三行
temp = P1;
temp = temp & 0xf0;
if(temp!=0xf0)
{
delay(10); // 延時消抖
temp = P1;
temp = temp & 0xf0;
if(temp!=0xf0)
{
temp = P1;
switch(temp) //掃描列
{
case 0xeb:
key = 7;
break;
case 0xdb:
key = 8;
break;
case 0xbb:
key = 9;
break;
}
while(temp!=0xf0) //等待按鍵釋放
{
temp = P1;
temp = temp & 0xf0;
}
}
}
P1 = 0xf7; //掃描第四行
temp = P1;
temp = temp & 0xf0;
if(temp!=0xf0)
{
delay(10); // 延時消抖
temp = P1;
temp = temp & 0xf0;
if(temp!=0xf0)
{
temp = P1;
switch(temp) //掃描列
{
case 0xe7:
key = 0;
break;
case 0xd7:
key = 0;
break;
case 0xb7:
key = 0;
break;
}
while(temp!=0xf0) //等待按鍵釋放
{
temp = P1;
temp = temp & 0xf0;
}
}
}
return key;
}
- 在主程序循環中,首先調用dis_set()函數顯示用戶設定溫度;
for(i=20;i>0;i--)
dis_set(key1, key2); //顯示用戶設定的溫度
//顯示設定溫度函數
void dis_set(uchar k1, uchar k2)
{
display2(1, k1);
display2(2, k2);
display2(0, k1);
}
//設定溫度數據顯示函數
void display2(uchar num, uchar tem_data)
{
if(num==0)
{
S1 = 1;
S2 = 1;
delay(5);
}
if(num==1)
{
S1 = 0;
S2 = 1;
P3 = table[tem_data]; //table為 0-9的16進制編碼表
delay(5);
}
else if(num==2)
{
S1 = 1;
S2 = 0;
P3 = table[tem_data];
delay(5);
}
}
然后再從溫度傳感器獲取當前溫度,獲取當前溫度的流程如下圖所示,先調用DSreset()函數進行溫度傳感器的初始化,再調用temwrite()函數,對傳感器寫入溫度轉換的指令,進行溫度獲取和轉換,然后調用get_tem()函數對傳感器寫入讀取寄存器指令,從寄存器中讀取存儲的溫度數據,并對該數據進行精度轉換處理,最后獲得一個保留了1位小數的當前溫度數據;
temchange(); //獲取當前溫度
//溫度獲取和轉換函數
void temchange(void)
{
DSreset();
delay(1);
temwrite(0xcc); //寫跳過ROM指令
temwrite(0x44); //寫溫度轉換指令
}
//讀取寄存器中存儲的溫度數據
uint get_tem(void)
{
uchar l8,h8;
DSreset();
delay(1);
temwrite(0xcc); //寫跳過ROM指令
temwrite(0xbe); //寫讀寄存器指令
l8 = temread(); //讀低8位數據
h8 = temread(); //讀高8位數據
tem = h8;
tem = tem<<8;
tem = tem|l8; //合成一個16位數據
f_tem = tem*0.0625;
tem = f_tem*10+0.5; //*10用于保留1位小數點,+0.5用于四舍五入
return (tem);
}
DS18B20溫度傳感器的基本操作代碼如下,各項操作要嚴格遵守DS18B20溫度傳感器的時序圖,延時時間要足夠,可以根據使用的主控芯片適當地修改循環的次數來調整延時。
初始化
//溫度傳感器初始化
uint DSreset(void)
{
uint i;
DS = 0;
i = 73;
while(i>0)
i--;
DS = 1;
i = 0;
while(DS)
{//等待DS18B20拉低總線
delay(1);
i++;
if(i>10)
{
return 0;//初始化失敗
}
}
DS = 1;
return 1;//初始化成功
}
讀1位數據
//讀1位數據
bit temreadbit(void)
{
uint i;
bit tem_bitdata;
DS = 0;
i++; //延時
DS = 1;
i++;
i++;
tem_bitdata = DS;
i = 10;
while(i>0)
i--;
return(tem_bitdata);
}
讀1字節數據
//讀1字節數據
uchar temread(void)
{
uint i;
uchar j,tem_data;
for(i=1;i<=8;i++)
{
j = temreadbit();
tem_data = (j<<7)|(tem_data>>1); //移位,讓最低位在最后面
}
return (tem_data);
}
寫1字節數據
//寫1字節數據
void temwrite(uchar tem_data)
{
uint i;
uchar j;
bit send_bitdata;
for(j=1;j<=8;j++)
{
send_bitdata = tem_data&0x01; //取要發送數據的最低位
tem_data = tem_data>>1; //右移一位
if(send_bitdata) //寫1
{
DS = 0;
i++;
i++;
DS = 1;
i = 10;
while(i>0)
i--;
}
else //寫0
{
DS = 0;
i = 10;
while(i>0)
i--;
DS = 1;
i++;
i++;
}
}
}
- 獲取完當前溫度,調用dis_tem()函數顯示當前溫度;
for(i=20;i>0;i--) //顯示當前溫度
dis_tem(get_tem());
//顯示當前溫度函數
void dis_tem(uint t)
{
uchar i;
i = t/100; //取溫度的十位
display1(1,i);
i = t%100/10; //取溫度的個位
display1(2,i+10);
i = t%10; //取溫度的小數點后一位
display1(3,i);
}
//當前溫度數據顯示函數
void display1(uchar num, uchar tem_data)
{
WE = 1; //選位,低電平有效
P0 = ~((0x01)<<(num));
WE = 0;
DU = 1; //選段,高電平有效
P0 = table[tem_data];
DU = 0;
delay(10);
}
- 將當前溫度和用戶設定溫度傳入deal()函數,進行恒溫控制,在恒溫控制函數deal()中,根據判斷當前溫度和用戶設定溫度之間的差值進行不同的處理,如果當前溫度小于用戶設定溫度,就進行升溫處理,即紅燈閃爍一次,每閃爍一次溫度上升0.5°,如果當前溫度大于用戶設定溫度,就進行降溫處理,即綠燈閃爍一次,每閃爍一次溫度下降0.5°,如果當前溫度與用戶設定溫度想等,則不做處理,只顯示溫度;
void deal(uint t, uint t_set)
{
uchar i;
if(tt_set)
{
work(15, 0x40); //降溫
}
else
{
i = 15;
while(i--)
{
dis_tem(tem_set);
dis_set(key1, key2);
}
}
}
//升溫、降溫模塊
void work(uint s, uchar led)
{
uchar i;
if(led==0x20)
{
i = s;
led0 = ~(led0); //燈亮
tem = tem+5;
while(i--)
{
dis_tem(tem);
dis_set(key1, key2);
}
led0 = ~(led0); //燈滅
i = s;
while(i--)
{
dis_tem(tem);
dis_set(key1, key2);
}
}
else
{
i = s;
led1 = ~(led1); //燈亮
tem = tem-5;
while(i--)
{
dis_tem(tem);
dis_set(key1, key2);
}
led1 = ~(led1); //燈滅
i = s;
while(i--)
{
dis_tem(tem);
dis_set(key1, key2);
}
}
}
- 進行一次恒溫控制后,系統又回到主程序循環的起始點,不斷重復上述3-5步驟,使溫度保持在用戶設定的溫度,達到恒溫的效果。



 返回頂部
返回頂部 刷新頁面
刷新頁面 下到頁底
下到頁底